Welcome to EEE Interview Tips
For Your Pre-Professional Preparation!
Download EEEBooks
To Download Electrical and Electronics Ebooks click the "EEE Library" menu! Enjoy!!
EEE Interview Tips
Leave Your Comments, Views And Questions.
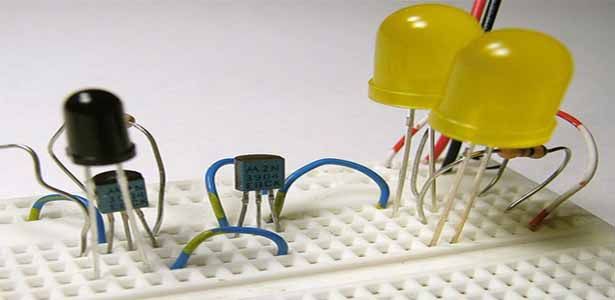
Learn to make Electronics
Burn things out, mess things up - that's how you learn to Make Electronics! Enjoyy!!
EEE Forum
Drop your Ideas, Thoughts, Questions and Comments!
September 11, 2013
September 7, 2013
Useful Electrical Equations!
Useful Electrical Equations:
· For Sinusoidal Current: Form Factor = RMS Value/Average Value = 1.11
· For Sinusoidal Current: Peak Factor = Max Value/RMS Value = 1.414
· Average Value of Sinusoidal Current (Iav) = 0.637 x Im (Im = Max.Value)
· RMS Value of Sinusoidal Current (Irms) = 0.707 x Im (Im = Max.Value)
· A.C Current = D.C Current/0.636.
· Phase Difference between Phase = 360/ No of Phase (1 Phase=230/1=360°, 2 Phase=360/2=180°)
· Short Circuit Level of Cable in KA (Isc) = (0.094 x Cable Dia in Sq.mm) /√ Short Circuit Time (Sec)
· Max.Cross Section Area of Earthing Strip (mm2) = √(Fault Current x Fault Current x Operating Time of Disconnected Device ) / K
K = Material Factor, K for Cu = 159, K for Al = 105, K for steel = 58 , K for GI = 80
· Most Economical Voltage at given Distance = 5.5 x √ ((km/1.6) + (kw/100))
· Cable Voltage Drop (%) =
(1.732 x current x (RcosǾ+jsinǾ) x 1.732 x Length (km) x 100) / (Volt(L-L) x Cable Run.
· Spacing of Conductor in Transmission Line (mm) = 500 + 18 x (P – P Volt) + (2 x (Span in Length)/50).
· Protection radius of Lighting Arrestor = √h x (2D-h) + (2D+L).
Where h= height of L.A, D-distance of equipment (20, 40, 60 Meter), L=V x t (V=1m/ms, t=Discharge Time).
· Size of Lighting Arrestor = 1.5x Phase to Earth Voltage or 1.5 x (System Voltage/1.732).
· Maximum Voltage of the System = 1.1xRated Voltage (Ex. 66KV = 1.1 × 66 = 72.6KV)
· Load Factor = Average Power/Peak Power
· If Load Factor is 1 or 100% = This is best situation for System and Consumer both.
· If Load Factor is Low (0 or 25%) = you are paying maximum amount of KWH consumption. Load Factor may be increased by switching or use of your Electrical Application.
· Demand Factor = Maximum Demand / Total Connected Load (Demand Factor <1)
· Demand factor should be applied for Group Load
· Diversity Factor =
Sum of Maximum Power Demand / Maximum Demand (Demand Factor >1)
Diversity factor should be consider for individual Load
· Plant Factor (Plant Capacity) = Average Load / Capacity of Plant
· Fusing Factor = Minimum Fusing Current / Current Rating (Fusing Factor>1).
· Voltage Variation (1 to 1.5%) = ((Average Voltage – Min Voltage) x 100)/Average Voltage
Ex: 462V, 463V, 455V, Voltage Variation= ((460 – 455) x 100)/455 = 1.1%.
· Current Variation (10%) = ((Average Current – Min Current) x 100)/Average Current
Ex: 30A,35A,30A, Current Variation = ((35-31.7) x 100)/31.7 = 10.4%
· Fault Level at TC Secondary
= TC (VA) x 100 / Transformer Secondary (V) x Impedance (%)
Motor Full Load Current = Kw /1.732 x KV x P.F x Efficiency
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)